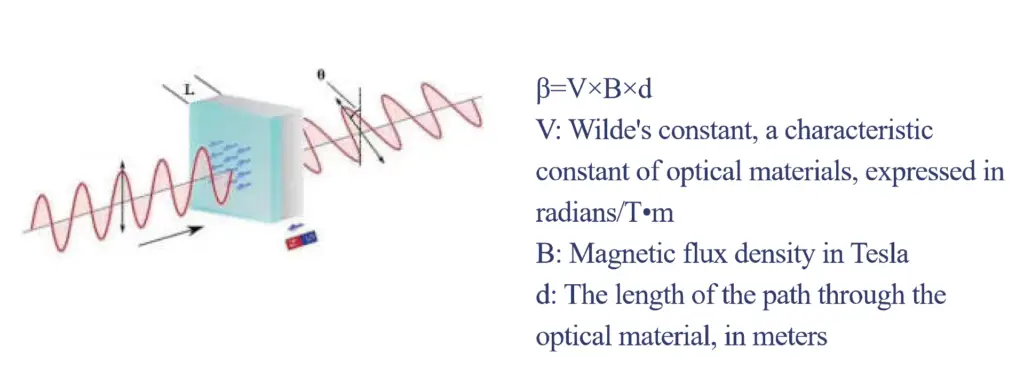
Magneto-optic devices operate on the principles of the Faraday Effect, which involves the interaction of light waves with magnetic fields in a medium. When light propagates through a magneto-optic material, the plane of polarization rotates linearly, proportionally to the applied magnetic flux density. This rotation is mathematically expressed as:
β = V × B × d
The Faraday Effect is exploited in optical systems to mitigate return light and its adverse effects. Magneto-optic devices are indispensable in applications requiring high isolation, minimal return loss, and stable performance, ensuring superior operation in laser systems.

Magneto-optic devices serve crucial roles across industries, including telecommunications, defense, medical imaging, and laser manufacturing.