Introduction
Accurate analysis of coupling efficiency is essential for designing high-performance fiber coupling systems. This article explores the methodologies for evaluating single-mode fiber coupling efficiency using optical simulation tools. By leveraging various computational approaches, including Gaussian beam propagation, single-mode fiber coupling, and physical optics propagation, we aim to optimize coupling performance while accounting for reflection losses and material absorption.
1. Setting Up the Fiber Coupling System
This case study focuses on a commercial fiber coupling system that connects two Corning SMF-28e fibers using a precision-engineered microlens array. The setup follows a rigorous design methodology to ensure high coupling efficiency and system symmetry.
System Specifications
| Component | Specification |
|---|---|
| Single-Mode Fiber | Corning SMF-28e |
| Numerical Aperture | 0.14 |
| Core Diameter | 8.2 µm |
| Mode Field Diameter (@1.31 µm) | 9.2 ± 0.4 µm |
| Microlens Array | SUSS MicroOptics SMO399920 |
| Substrate Material | Fused Silica |
| Substrate Thickness | 0.9 mm |
| Internal Transmission | >0.99 |
| Lens Diameter | 240 µm |
| Lens Pitch | 250 µm |
| Radius of Curvature | 330 µm |
| Numerical Aperture | 0.17 |
The optical system is designed to maintain symmetry, ensuring efficient coupling in both directions. Optimization techniques are employed to refine parameters such as lens separation and beam alignment for optimal performance.
2. Gaussian Beam Analysis for Fiber Coupling
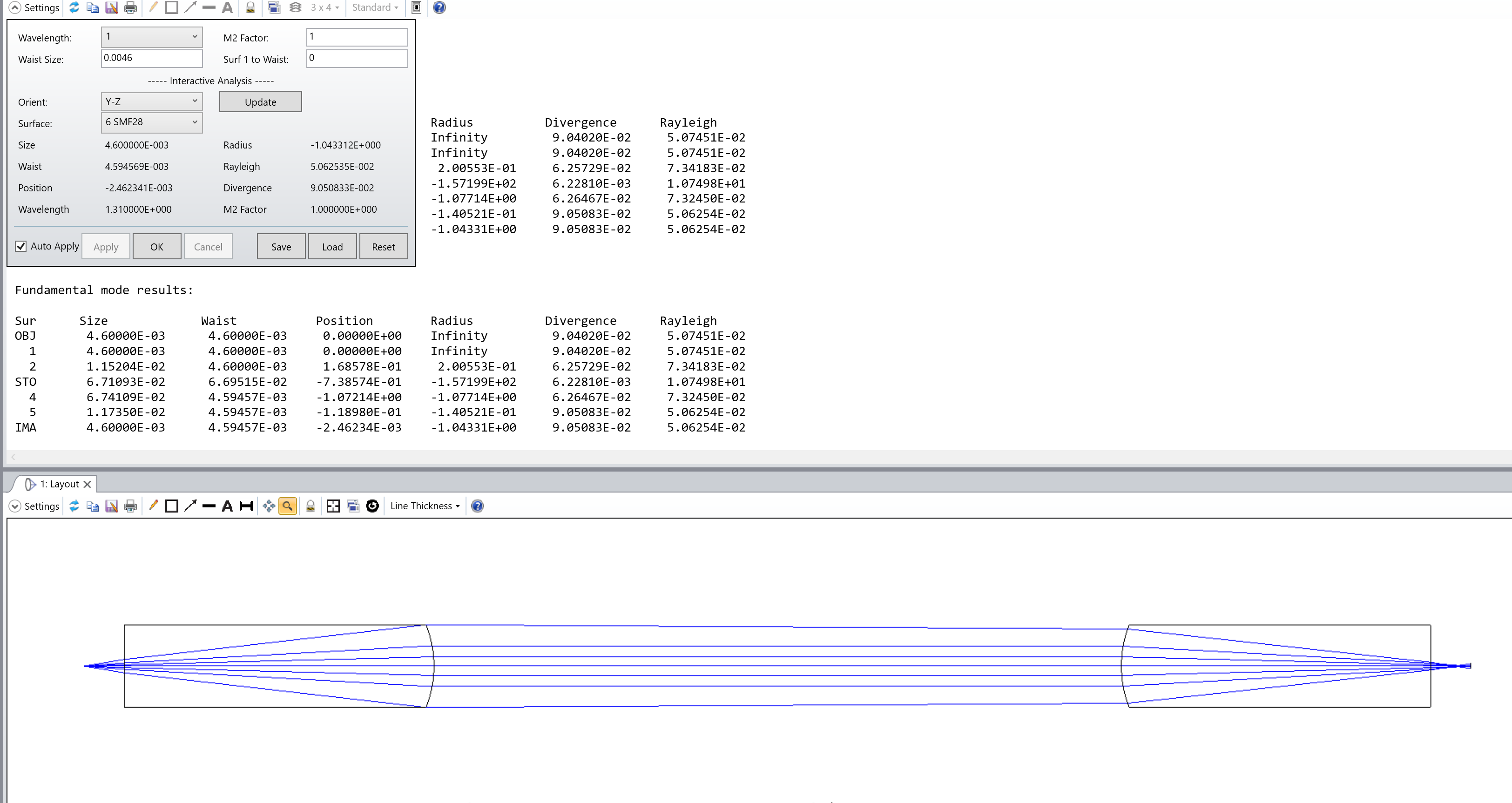
The Paraxial Gaussian Beam Calculation provides an initial assessment of coupling efficiency by analyzing beam waist positioning and propagation through the optical system.
Key Observations
- The mode field diameter at 1.31 µm is 9.2 ± 0.4 µm.
- The beam waist is positioned at the source fiber, with a radius of 4.6 µm.
- The energy distribution follows a Gaussian profile, ensuring minimal beam truncation.
By optimizing the fiber-to-lens distance, we achieve a more uniform beam profile, improving coupling efficiency and minimizing optical aberrations.
3. Single-Mode Fiber Coupling Calculation
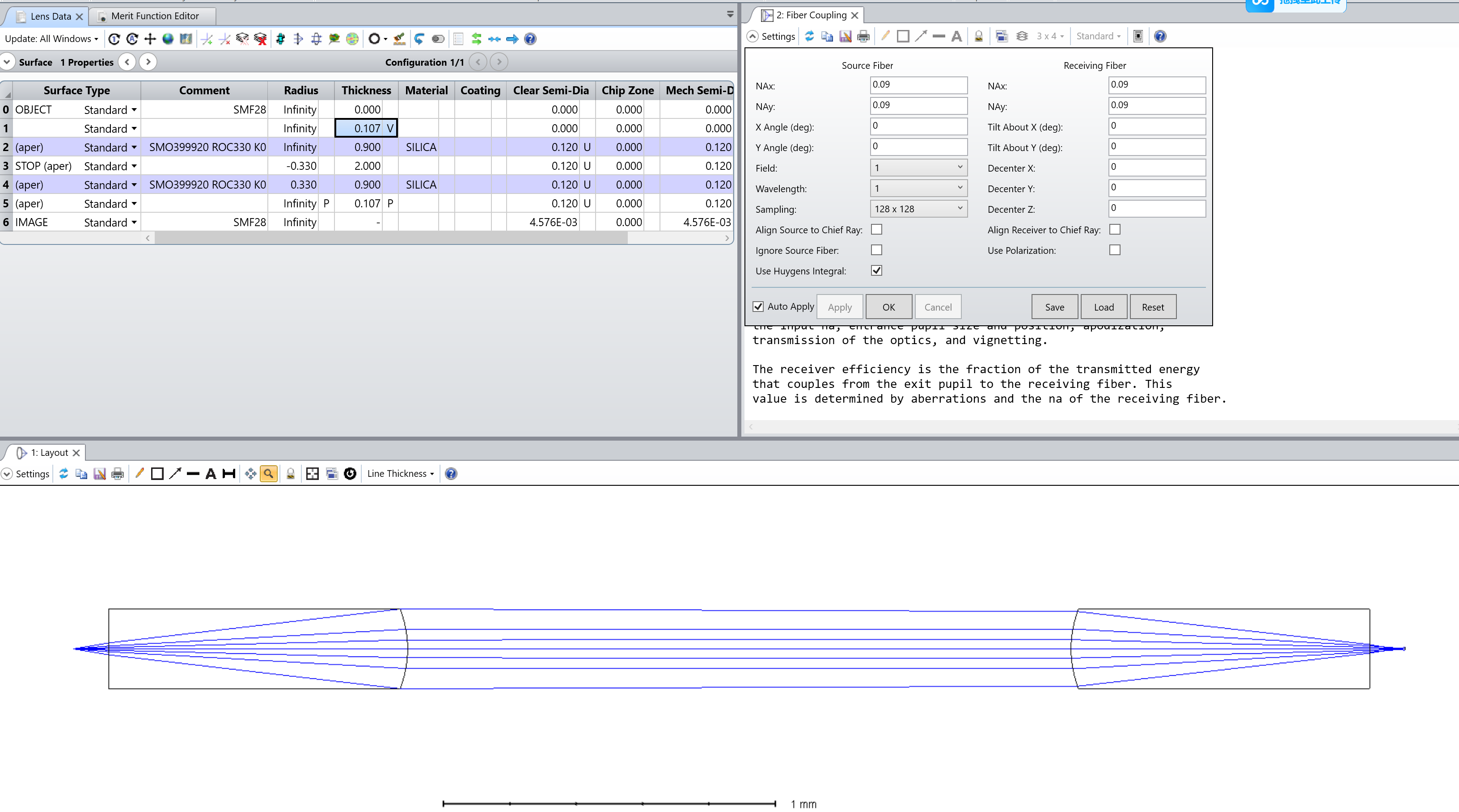
This method evaluates coupling efficiency by analyzing energy transport and mode matching between the fiber and optical system.
Optimization Parameters
- Energy Transport Efficiency (S): Measures the fraction of optical power transmitted through the system.
- Mode Matching (T): Quantifies the overlap between the wavefront and the receiving fiber mode.
- Total Coupling Efficiency (S × T): Represents the final transmission efficiency.
By adjusting the fiber-lens spacing, we achieved an optimized coupling efficiency of 0.107 mm, refining the system’s performance.
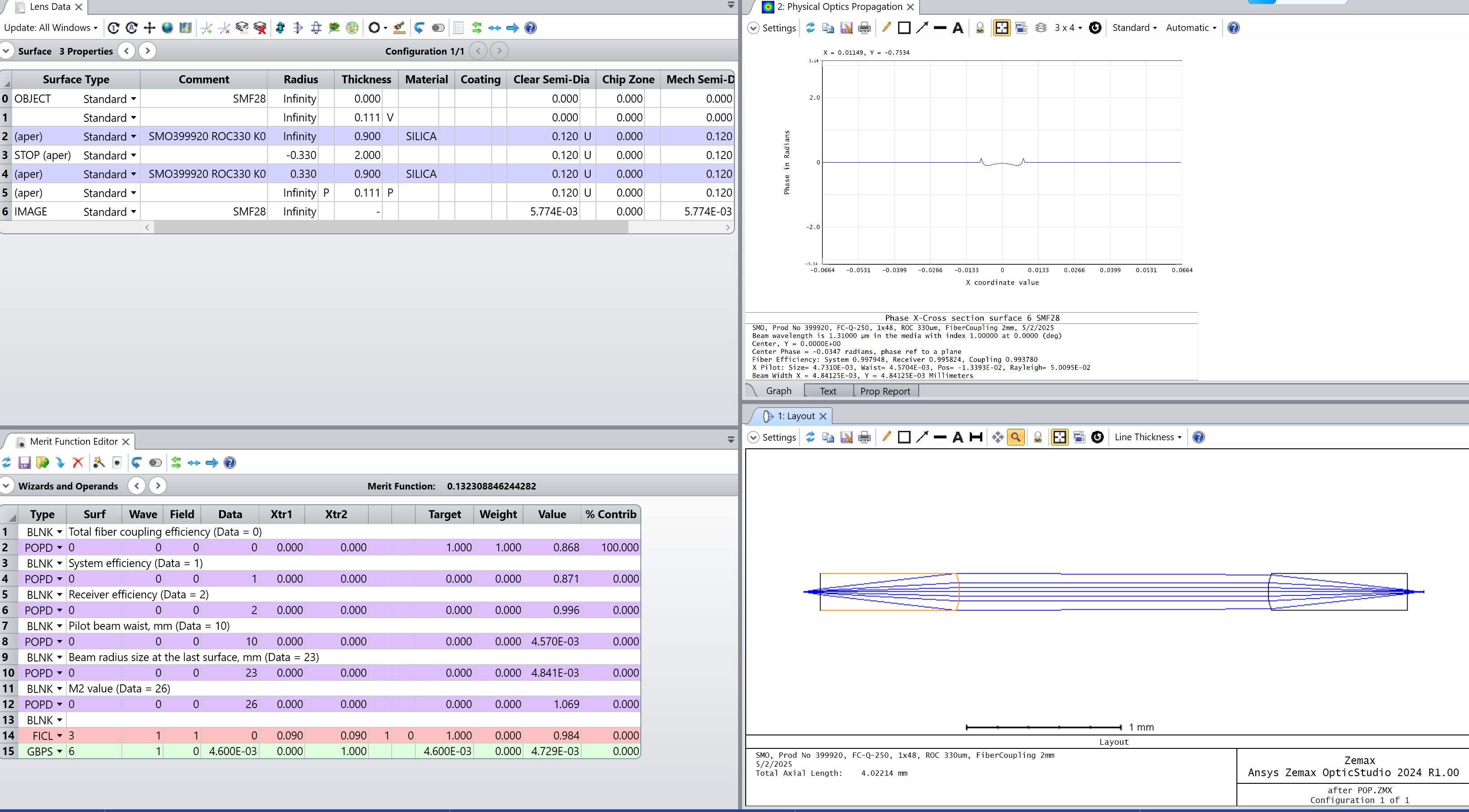
4. Advanced Analysis with Physical Optics Propagation (POP)
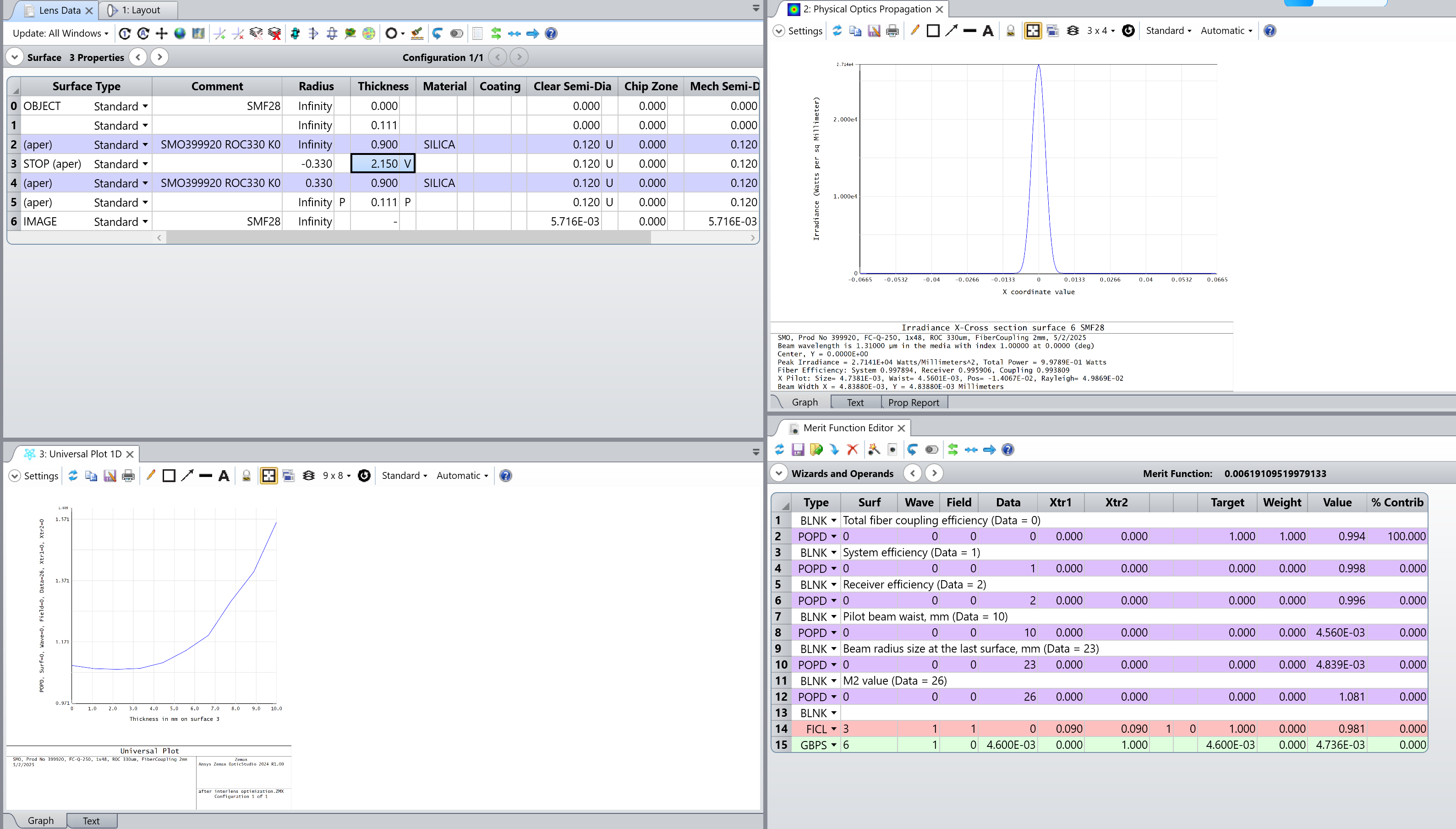
For a more comprehensive evaluation, Physical Optics Propagation (POP) is utilized, offering benefits such as:
- Full-wave analysis beyond Gaussian beam assumptions.
- Precise modeling of diffraction effects and aperture truncation.
- Compatibility with external simulation tools for integrated optical devices.
Key Findings from POP Analysis
- The Gaussian mode maintains a high M² quality factor of 1.086.
- Phase aberrations, including focus and spherical distortions, are minimized through lens alignment adjustments.
- A refined lens-lens spacing of 2.15 mm optimizes fiber coupling efficiency, ensuring stable system performance.
5. Accounting for Optical Losses
To enhance coupling efficiency, we address surface reflections and bulk absorption by incorporating polarization-dependent coatings.
Performance Improvements with Coatings
| Coating Type | Transmission Improvement |
|---|---|
| MgF₂ AR Coating | Efficiency increase to 93% |
| HEAR1 High-Performance Coating | Efficiency improvement to 99% |
Applying anti-reflective coatings on optical surfaces reduces Fresnel losses and improves transmission stability, making it ideal for high-power fiber coupling applications.
Conclusion
Optimizing single-mode fiber coupling requires a multi-step analysis, integrating Gaussian beam methods, mode-matching calculations, and full-wave optical propagation techniques. By fine-tuning parameters such as fiber-lens distance, optical alignment, and coatings, we achieve high coupling efficiency, ensuring superior system performance for industrial, telecommunications, and scientific applications.





